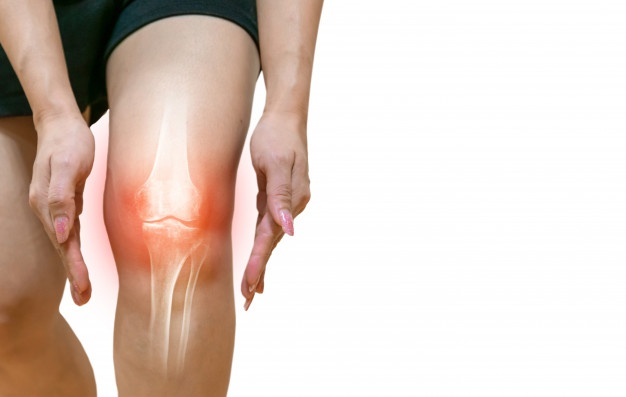
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common articular disease worldwide. Prevalence increases with age.
Symptoms
Pain is the main reason for patients to seek medical attention. Initially, pain occurs during activity, which can be relieved by rest and may respond to simple analgesics. Morning stiffness in the joint usually lasts for less than half an hour.
Joints may become unstable with disease progression; therefore, the pain can become more prominent (even at times of rest) and may not respond to medications.
Physical examination findings are mostly limited to the affected joints. In most cases, erythema or warmth over the joint does not occur; however, an effusion and limitation of joint motion or muscle atrophy around a more severely affected joint may occur.
Risk factors
Age, obesity, female sex, trauma, infection, repetitive occupational trauma, genetic factors, history of inflammatory arthritis, neuromuscular disorder and metabolic disorder.
Treatment
Patients should rest or a change in activities to avoid provoking osteoarthritis pain. This may include modifications in work or sports activities from high-impact activities to low-impact exercises. A weight loss program may be recommended.
– Simple things you can do : Make sure that you do not keep your leg bent in the same position for long periods. Use a stick to take the weight off the joint if you need to.
– Physical therapy : In OA of the knee, disuse atrophy of muscles may occur. These muscles help protect the articular cartilage from further stress. Physical therapy improves muscle strength, mobility, function and ease pain.
– Pharmacologic therapy : The goals of treatment are pain alleviation and improvement of functional status. Begin treatment with acetaminophen for mild or moderate pain without apparent inflammation. If clinical response to acetaminophen is not satisfactory, consider physician consultation.
– Surgical Care : This may help patients with OA of the knee, especially with symptoms that are recalcitrant to pharmacologic agents or physical therapy.