Knowledge
Caregiver Stress
Who is a caregiver? You´re a caregiver if you give basic care to a person who has a chronic medical condition. A chronic condition is an illness that lasts for a long period of time or doesn´t go away. Some examples of chronic conditions are cancer, stroke, multiple sclerosis, dementia, diabetes and Alzheimer´s disease. If you´re a caregiver, you may
Bedsores, Pressure Sores
Bed sores can occur when a person is bedridden, unconscious, unable to sense pain, or immobile. Bed sores are ulcers that occur on areas of the skin that are under pressure from lying in bed, sitting in a wheelchair, or wearing a cast for a prolonged period of time. Why does a bed sore develop? A bed sore develops when
Diabetes mellitus (DM)
Diabetes is a lifelong condition where your body does not produce enough insulin, or your body cannot use the insulin it produces. Your body needs insulin to change the sugar from food into energy. When you don´t have enough insulin, the sugar stays in your blood so that your “blood sugar level” gets too high. High blood sugar levels over
heart attack
A heart attack is the death of heart muscle due to the complete blockage of a diseased coronary artery due to a blood clot. What causes it? Coronary artery disease (CAD) is by far the commonest cause. Coronary arteries become narrowed, usually as a result of fatty cholesterol deposits (plaque) in the arterial wall, which bulge inwards and partly obstruct
Parkinson’s disease
What is Parkinson´s disease? Parkinson´s disease is a disorder of the central nervous system which includes the brain and spinal cord. Parkinson´s disease is a movement disorder and its symptoms get worse over time. Parkinson´s disease affects both men and women almost equally. Although people of any age may develop Parkinson´s disease, it is usually seen in people over the
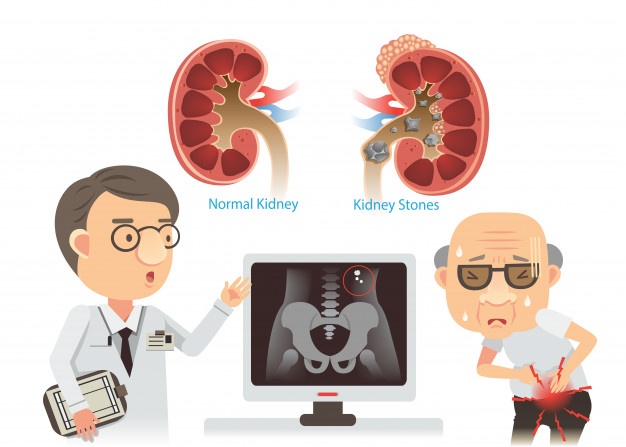
Chronic renal failure (Chronic kidney failure)
Your kidneys are two bean-shaped organs, each about the size of your fist. They´re located at the back of your upper abdomen, on either side of your spine. Your kidneys are part of a system that removes excess fluid and waste material from your blood. Chronic renal failure (renal = kidney) is a gradual and progressive loss of the ability
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a lung disease in which the lungs are damaged, making it hard to breathe. In COPD, the airways—the tubes that carry air in and out of your lungs—are partly obstructed, making it difficult to get air in and out. What Causes COPD? Cigarette smoking is the most common cause of COPD. Most people with
Hip fractures
Hip fractures (broken hips) are most often caused by a fall in elderly people. It does not have to be a major fall for an elderly person to break a hip. Other ways for a hip to break could be from car accidents or if the bone has become weakened from tumor or infection. Risk Factors A broken hip in
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common articular disease worldwide. Prevalence increases with age. Symptoms Pain is the main reason for patients to seek medical attention. Initially, pain occurs during activity, which can be relieved by rest and may respond to simple analgesics. Morning stiffness in the joint usually lasts for less than half an hour. Joints may become unstable with
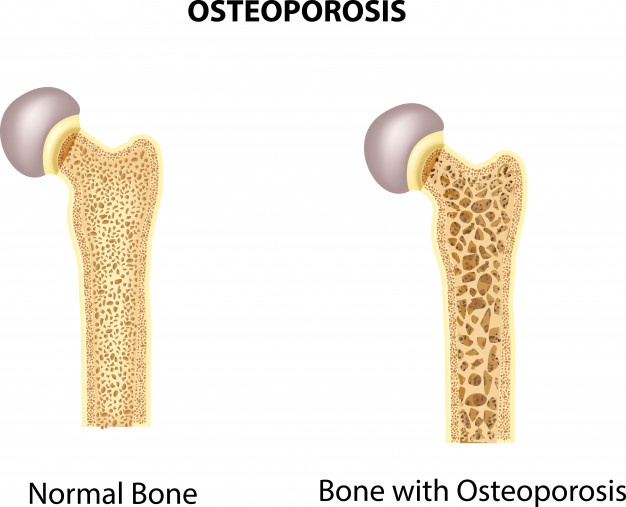
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a skeletal disease in which bones become thinner and more porous, and more prone to fracture. Osteoporotic fractures most commonly occur in the hip, spine, and wrist. The disease is usually painless until a bone breaks or fractures. Signs and symptoms Osteoporosis itself has no specific symptoms; its main consequence is the increased risk of bone fractures. Typical